
There are many information security standards that UK businesses can work with to protect themselves from cyber related risks. If you’re looking for straightforward measures, which will provide a great starting point and demonstrate compliance in the industry, don’t fret!
This article covers some of the most popular cyber security standards out there so it’s okay if your head is spinning at all this information overload right now – we have got you covered on everything from securing data such as passwords and encryption keys to backing up critical systems.
What are the cyber security standards?
Like any other industry standards, cyber security standards are some of the critical decisions and specifications made to protect the cyber arena from growing cyber threats. The security industry offers a variety of standards related to IT security, privacy, physical security, data protection, and other aspects of security control management and maintenance for overall assets and organisation.
Cyber security standard is a generic set of rules, defined for the execution of certain controls to accomplish the information security principle i.e., Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability of data within the organisation’s physical and virtual network. The information security standards also have some of the principles, guidelines, best practices, frameworks, methods, and approaches to address the security mechanism implementations.
Security standards address its rules and guidelines to all sizes of enterprises irrespective of their driving industry and sector. It has the least set of components and controls required for every organisation which they must include in their business as a cyber security risk mitigation strategy to be compliant with the standard. It efficiently reduces the complexity of security deployments by offering simple methods and structures for advancement as well as work as a business continuity plan in the worst situation such as a data breach or cyber attack.
Cyber security standard is defined as
“a published specification that establishes a common language, and contains a technical specification or other precise criteria and is designed to be used consistently, as a rule, a guideline, or a definition.”
Incorporating cyber security standards in the business strategy is one of the crucial ways for the enterprise to ensure that all of the policies, data, and assets such as systems, network devices, security solutions, etc. are safe and fulfilling their operation in a controlled and measurable manner. These standards play a significant role in defining the security posture and engaging the compliance requirements of any organisation.
On a high level, security standards might seem like regulatory formalities but in reality, it significantly wipes out risk, threats and strengthens the overall information security posture of infrastructure, network, and the entire enterprise.
What is the UK equivalent of NIST?
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) cyber security framework published by the US which is now translated and used worldwide by many of countries including Japan, Italy, etc. NIST provides guidelines for small and midsize businesses to large enterprises to enhance the protection, mitigate cyber attack surface and improve the risk management capabilities.
It has divided the cyber function into five categories, i.e., Identity, Protect, Detect, Respond and Recover. Once done appropriately, all activities strengthen the enterprise’s security structure. Many businesses now follow the NIST framework during risk assessment exercises as part of their risk management programme.
Where most of the countries translated and adopted the NIST security policy framework, the United Kingdom UK government brought out and published its national compliances in the form of Minimum Cyber Security Standard in connection to the NIST cyber security framework to mandate the implementation of standards across all UK government departments as the minimum-security practice.
European Commission has introduced EU-wide The Digital Operational Resilience Act, that’s worth a read.
What is the minimum cyber security standard?
Minimum cyber security standard MCSS was published in 2018 in collaboration with the National Cyber Security Center (NCSC) to introduce the minimum set of cyber hygiene with the closest approximation of the international cyber security frameworks. It is supposed to be included in the government functional standard for security by UK Gov.
MCSS has shared a functional standard for security that the UK government bodies, agencies, and suppliers must incorporate in their business’s strategy wherever possible. These functional standards for security are categorised into five areas i.e., identity, protect, detect, respond and recover. When incorporated into information security policies, these control areas help investigate, measure, and mitigate the cyber threats relevant to their attack vectors.
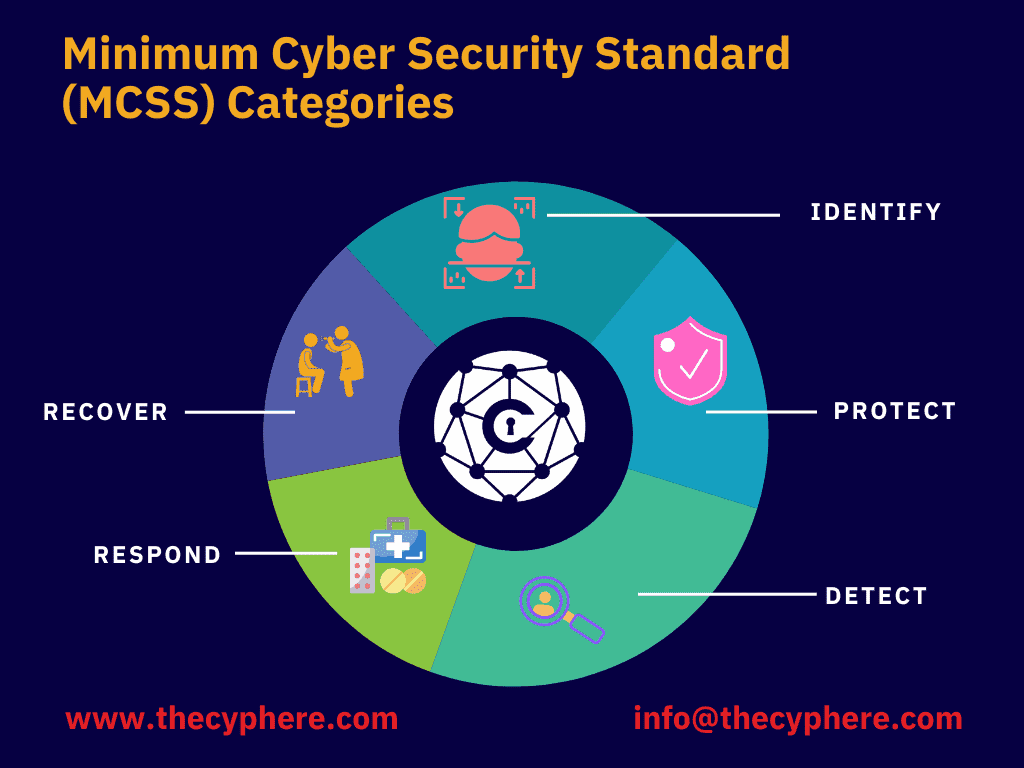
Five categories of Minimum Cyber Security Standard
Identify
The first category of minimum cyber security standard is identification. To protect your assets, you must know where your data is stored, who is responsible for data storage, and who can access the data.
Who is responsible?
It is all about identifying the individuals who are responsible for ensuring personal or sensitive data security. It also includes the department’s identification who relies upon third-party for data security. Suppose any of the departments or individuals maintain the information security via a third party or any vendor. In that case, it also applies to them to guarantee the third party follows the policies and has valid cyber essentials.
Furthermore, the organisations or government departments have to guarantee that the responsible individual for maintaining the data security must have suitable cyber essentials training and security awareness in terms of holding sensitive data, and the same person must promote cyber hygiene and practice across the business and department.
Where is sensitive data?
The organisation must know where and how they secure their data. Similar to the GDPR requirements, the minimum cyber security standard mandates the organisation to inform the reason for data collection and processing. In addition to it, they must classify the data on the basis of their importance and potential impact in case of a data breach.
Who can access the data?
The minimum cyber security standard focuses on maintaining access to sensitive data. The organisations and departments must have a clear policy to manage and maintain data privacy and protection. Therefore, they must implement the least privilege rule to have minimum access to sensitive information and other related services. The department must also ensure that only relevant and needed access is granted to the user and any excessive permissions are reviewed and revoked promptly.
Protect
This category focuses and directs the organisation/departments to protect the data and assets from unauthorised access and cyber attacks. In the minimum cyber security standard, the regulatory body forces the organisations to take suitable and all necessary actions to protect data exposure.
The department should execute an authentication and authorisation mechanism to protect sensitive information to allow legitimate access. Moreover, for exclusive or critical data protection, strict security restrictions such as Two-factor authentication must be imposed. To maintain the CIA of data, a department or organisation can create copies of data when any user makes data changes or modifies the file.
Vulnerable systems and services are prone to cyber threats and seek attacker attention; strict security controls, authorisation, and authentication will do nothing if the system or process itself is on the edge of open risk. MCSS particularised various ways to protect assets, systems, and services such as.
- Systems or services must be tested against known vulnerabilities and should be resilient enough to prevent intrusion and combat common cyber attacks.
- Outdated software or services should not be activated
- Software must remain updated.
- Run vulnerability scan regularly.
- Patch the vulnerable system and services.
- Monitor the accounts to spot authorised access trials.
- Regularly rotate passwords
Detect
Organisations or departments must have the log monitoring and auditing solution in place to detect suspicious traffic and keep track of activities, so they can quickly spot threats or attacks and take action. With the help of an audit and monitoring solution, the department can investigate the event log against the known cyber threat and attack vector.
It is entirely up to the enterprise how they choose and execute monitoring solutions according to their business nature, requirements and size. However, they must identify the cyber challenges and threats coming to them at their earliest to prevent damage and reduce the likelihood of attack.
Respond
The government agencies, organisations, and departments should have prepared security plans in place to resist cyber incidents. The incident response and management plan support the organisation in strategically handling cyber incidents. In order to respond to cyber attacks effectively, create a plan in advance with critical decisions and related employees’ roles and responsibilities. In addition, map out the pathway and actions that are important to do while reacting to the attack or any incident.
Additionally, do not forget to notify the concerning regulatory bodies such as Government security groups, law enforcement, ICO, national cyber security center, and others about the severity and impact of the attack. It is important to keep the incident response plan updates with the changing cyber attack trends and landscape.
Last but not least, Take notes of every cyber attack, note down the learned lesson, record every bit of incident, document all the strategies used in handling the attack and use all of the learning in improving incident response capabilities and create updated information security hygiene strategy.
Recover
In any event of security control failure or impactful cyber attacks, the organisation must take account of the incident and collaborate with the team to restore services or operations with minimum downtime. For this, they should have an appropriate contingency mechanism to recover from failure. Once it is done, they must investigate the incident, learn the reason for it, and improve the security strategy for the future.
What are the 10 Steps to Cyber Security?
To consolidate the UK government MCSS (Minimum Cyber Security Standard) into the business strategy, organisations can benefit themselves via the National Cyber Security Centre guidance that includes 10 steps to cyber security. This guideline was published in 2012, and today, it is being used by most of the FTSE (Financial Time Stock Exchange) firms.
The NCSC 10 steps of cybersecurity facilitate organisations to manage and maintain the risk according to business operations and sector. Along with this, it also helps businesses to respond and recover from cyber incidents. With the right incorporation of these 10 guidelines, the business’s cyberattack surface can be minimised to a considerable level.
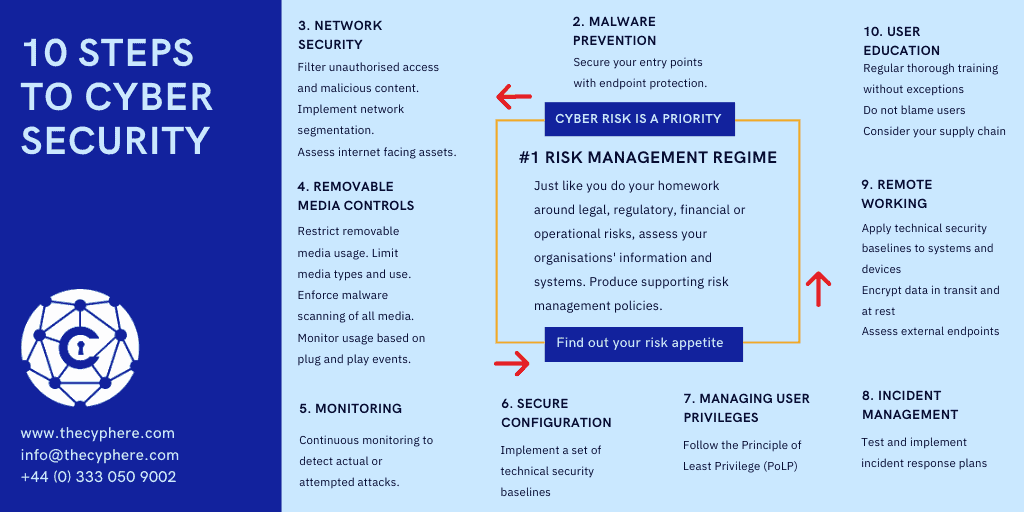
National Cyber Security Centre – 10 Steps to cybersecurity
The 10 steps to cyber security include the following best practices and approaches.
- Risk management
- Engagement and training
- Assets management
- Architecture and configuration
- Vulnerability assessment
- Identity and access management
- Data security
- Logging and monitoring
- Incident management
- Supply chain security
Read our detailed blog on 10 steps to cyber security to understand and grasp knowledge on combining NCSC guidelines into your business. You should head here if you want to strengthen your GRC (Governance, Risk and Compliance) areas.
Conclusion
Whether you’re a small business or a large enterprise, cyber security is the only way to ensure business security in the new era of digital presence. As a compliance solution provider, Cyphere has expertise in deploying standards in all types of industries to strengthen the business’s online presence. Adhering to compliance not only prevents you from penalties but also enhances brand visibility, gains customer trust and shields business reputation.
Get in touch to discuss your concerns regarding your security compliance requirements.
Shahrukh, is a passionate cyber security analyst and researcher who loves to write technical blogs on different cyber security topics. He holds a Masters degree in Information Security, an OSCP and has a strong technical skillset in offensive security.












