
In the present age, when data has become a significant aspect of every business application, more pieces of information have been stored and processed. The security and quality of that information are vital to protect the health of the data throughout its lifecycle. Implementing measures that preserve the integrity of the data is increasingly vital for organisations around the world. For a business, to keep its data intact, whether it is business data, health data, financial data or customer personal data, understanding the basics of data integrity and its concept can help to reduce the problems arising from the compromised accuracy and consistency of that data.
At Cyphere, as a cyber security services provider, we ensure that data integrity checks remain one of the top priorities for businesses where data sensitivity topic is in scope. This helps them ensure that critical data is not lost or tampered with and that they can trust the security of their systems.
In this article, you will find pretty much everything about data integrity. It includes
- what is meant by data integrity and its core concepts,
- the types of data integrity based on the business need,
- differences among data integrity, data quality and data security,
- risks to the data integrity loss,
- how to ensure the integrity of your systems and processes; and
- What does data integrity mean?
The term integrity means the state of being complete and correct. Data integrity is the protection of data’s reliability and trustworthiness throughout its lifecycle. The form of the data, i.e. whether the data is valid or not, is the accuracy of the data achieved or the validation is preserved, are all ensured with the help of data integrity mechanisms.
Data integrity checks help reduce cyber security concerns by ensuring that the data has not been tampered with while in transit. This helps to ensure that the data is accurate and can be trusted, which reduces the risk of any potential security breaches.
It ensures the completeness and quality of the data required mainly by the data-driven business. Decisions. Error checking and handling procedures are also based on data integrity principles.
Types of data integrity
The two types of data integrity mechanisms used in both hierarchical and relational databases are:
Physical integrity
Protecting the completeness and accuracy of data while it is being stored or retrieved is known as maintaining the physical integrity of that data. Common threats to compromising physical integrity include natural disasters, disruption to database functions, human error or power disruption.
Logical integrity
The logical integrity of data validates whether data is correct and accurate in these four specific contexts:
-
Entity integrity
A type of logical integrity in which a pair of unique values i.e. primary keys, identify pieces of data. These primary keys validate the data is not listed more than once in a table or that no field in a table is null. This mechanism is mainly used in relational systems which store data in tables.
-
Referential integrity
Referential integrity sets rules in a relational system that may include constraints to remove the entry of duplicate data, ensure that data is accurate, and/or reject the entry of data that doesn’t apply. To maintain the referential integrity stored in the database foreign keys are used which ensure that only authorized changes may occur.
-
Domain integrity
A domain is a set of adequate values that a column is allowed to contain. Domain integrity sets rules to include constraints and other measures to limit the format, type, and amount of data entered.
-
User-defined integrity
When specific business rules must be taken into account and incorporated into data integrity measures, user-defined integrity rules may apply that involves the constraints created by the user itself.
Is data integrity the same as data security or data quality?
Difference between data integrity and data security
Often people may confuse data integrity with data security as, to some degree, both are responsible for the protection and reliability of data. To highlight the main difference, data integrity ensures the trustworthiness of data, while data security is a vast area that mainly focuses on minimizing the risks of compromising the data.
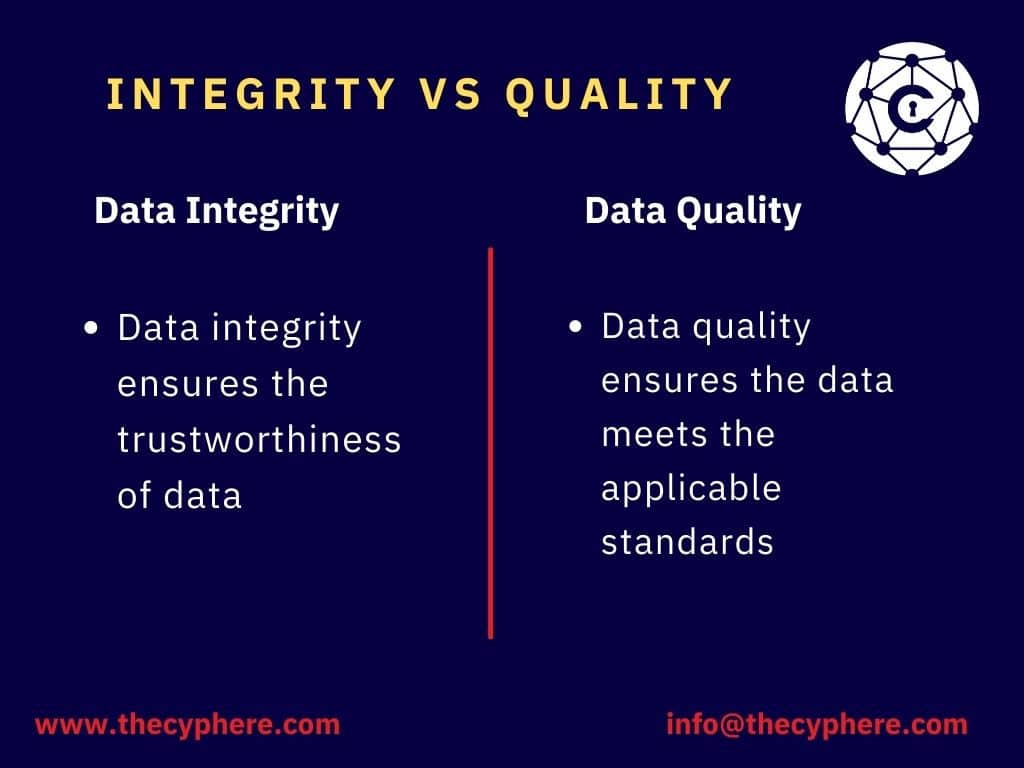
Difference between data integrity and data quality
Data quality is one of the facets of data integrity in which an organisation ensures the database meets the applicable standards to validate data lifecycle, relevance and reliability. Data quality measures the accuracy and reliability, while data integrity as full measures these two with the correctness, effectiveness, and completeness of data specific to the context.
Why is data integrity important?
Today, data is one of the valuable assets of any business. Whether targeting customers with personalized ads, researching medical cures, or confidential data for business transactions, data accuracy, security, and consistency are vital to performing all these actions.
Data integrity and cyber security
The whole concept of cyber security is based on a CIA triad, i.e. confidentiality, integrity and availability. As data integrity is integral to addressing cyber security procedures, it can be compromised in several ways, making the data integrity process a fundamental component of an organisation’s security protocols.
For addressing data integrity in basic cyber security practices, an organisation may need to deploy security controls including but not limited to encryption (data encrypted at rest or in transit makes it less vulnerable to alterations), data backup (data can be stored at an alternate location to retrieve lost data in case of any security incident), monitoring (identify any suspicious activity) and access control (regulates who or what can access or use data).
Data integrity and GDPR compliance
GDPR being the world’s strictest privacy law, has some important rules related to data integrity. Integrity is one of the principles of GDPR that states that personal data should be:
“processed in a manner that ensures appropriate security of the personal data, including protection against unauthorized or unlawful processing and against accidental loss, destruction or damage, using appropriate technical or organisational measures“.
Non-compliance with these requirements can make organisations liable for large penalties. Fortunately, GDPR has been flexible about what measures companies should take to ensure the integrity of data.
Data integrity risks
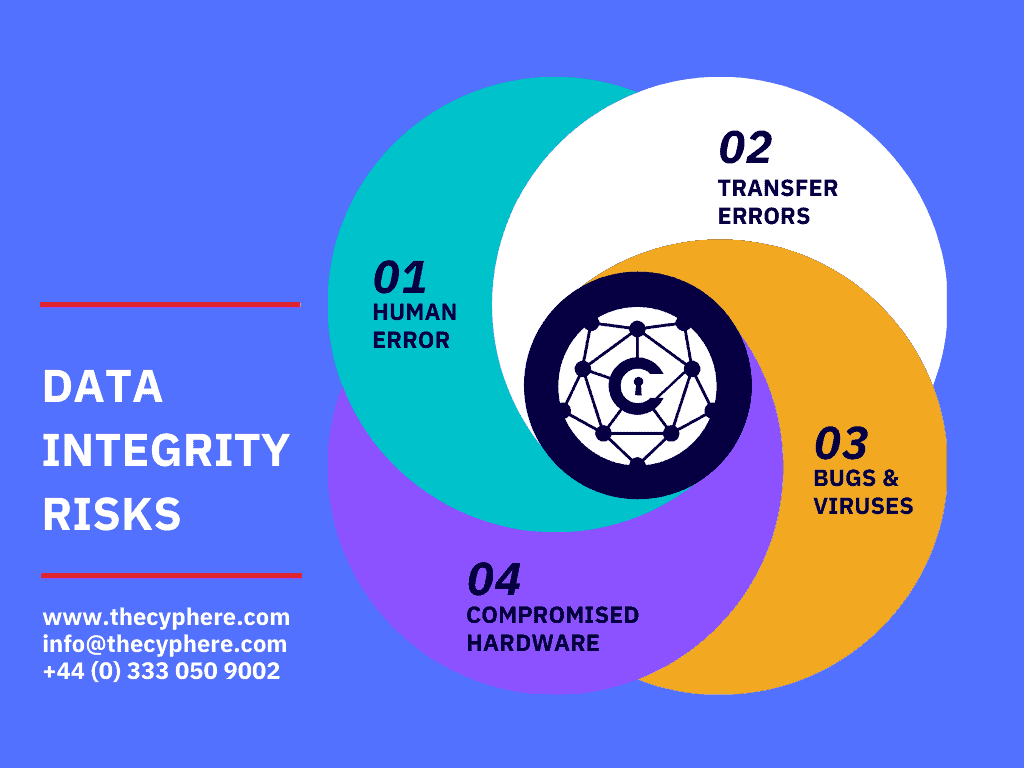
The importance of data integrity can be evaluated by looking at the high-risk factors bearing on the processing of stored data in a database. The most common high-risk factors are as follows:
1. Human error
Human error is one of the common factors to compromise the integrity of data. When users enter incorrect data, modify source data, or make mistakes during the implementation of procedures necessary for protecting data, data integrity has been compromised.
2. Transfer errors
While transferring the data from one location to another in a database, a transfer error has occurred. Transfer errors arise when a data element is present in the destination table but not in the source table in a relational database.
3. Bugs and viruses
Malware, viruses and compromised source code are pieces of harmful data files that can invade a computer and modify, delete, or steal data.
4. Compromised hardware
Sudden system or server crashes, lack of the use of server hardening practices and errors with how a computer or other device functions are examples of compromised hardware. Compromised hardware may process data incorrectly or incompletely, restrict or eliminate access to data, or make information hard to use stored in a database.
How do you ensure data integrity?
For any business, ensuring data integrity within the database is achieved by applying best practices and the standard rules throughout the data lifecycle.
The following key indicators may be helpful starting points for the companies :
- Create an inventory of privileged access rights, indicating who has access to what and when with the permission details.
- Create an inventory that includes data extraction, transformation and loading to another system.
- Terminate the access rights of the users who have left the job and delete the orphaned or dormant accounts.
- Create the list of the number of users that required access to production data to modify or correct them.
- Map the number of data security issues associated with data (Yearly or monthly).
- Create an index of inaccurate or inconsistent data.
- Calculate the percentage of the organisation or critical application data model that is incorporated by measures to protect the integrity of data.
- Create the procedures to maintain data integrity in databases and applications for addressing data accuracy and consistency.
- Perform several measures to detect unauthorized access to critical data.
- Perform several measures to detect unauthorized access to Operating systems.
- Create a process to detect changes that are not subject to change-control procedures.
- Conduct regular internal audits and place the audit trails in a secure location.
- Keep an eye on several press reports that arose from data integrity problems.
Final Thoughts
For every small to medium enterprise, ensuring data integrity is fundamental to addressing the accuracy and validity of business processes. According to McKinsey’s DataMatics survey (pdf), data-driven organisations are 23 times more likely to beat competitors in consumer acquisition, nine times more likely to retain consumers, and up to 19 times more profitable. This highlights the importance of data even for small businesses.
To ensure the security and quality of business data, the methods of assuring integrity play an important role thought the process. Whether it be addressing data integrity in GDPR compliance or deploying security controls like encryption, backup or access control to maintain integrity in business procedures, data integrity is critical yet manageable for any size of organisation.
Get in touch to schedule your organisation’s IT security health check and compare where you stand.
Shahrukh, is a passionate cyber security analyst and researcher who loves to write technical blogs on different cyber security topics. He holds a Masters degree in Information Security, an OSCP and has a strong technical skillset in offensive security.












