It is rightly said that the weakest link, even in a most cyber-secure environment, is the human being which renders the entire organisation as vulnerable as the weakest link. Playing games with the human mind and manipulating human thinking and psychology is extremely easy; hence, the human being is the lowest asset in a secure cyber environment.
This ease of manipulating human psychology makes social engineering and such attacks the most dangerous attack vector. Over the years, social engineering has been a significant cause of major cyber attacks, and in 2022, it remained one of the most common attacks against various industries. To keep your digital assets secure, we provide a range of cyber security services that are independent, vendor agnostic and reliable.
In this blog post, we will observe some of the recent social engineering attacks statistics to understand the root cause of social engineering is still relevant in today’s digital world.
But before we move deep into social engineering statistics for the last few years, let us first recap and revise what social engineering is.
What is social engineering?
Social Engineering is a technique that plays with and manipulates human psychology and mindset. It refers to the psychological deception to trick people into giving out confidential and sensitive data and information or performing actions that may compromise their or their organisation’s security.
The only objective of Social Engineering is financial gain, obtaining unauthorized access to confidential or sensitive information and systems, or spreading malware or other malicious content.
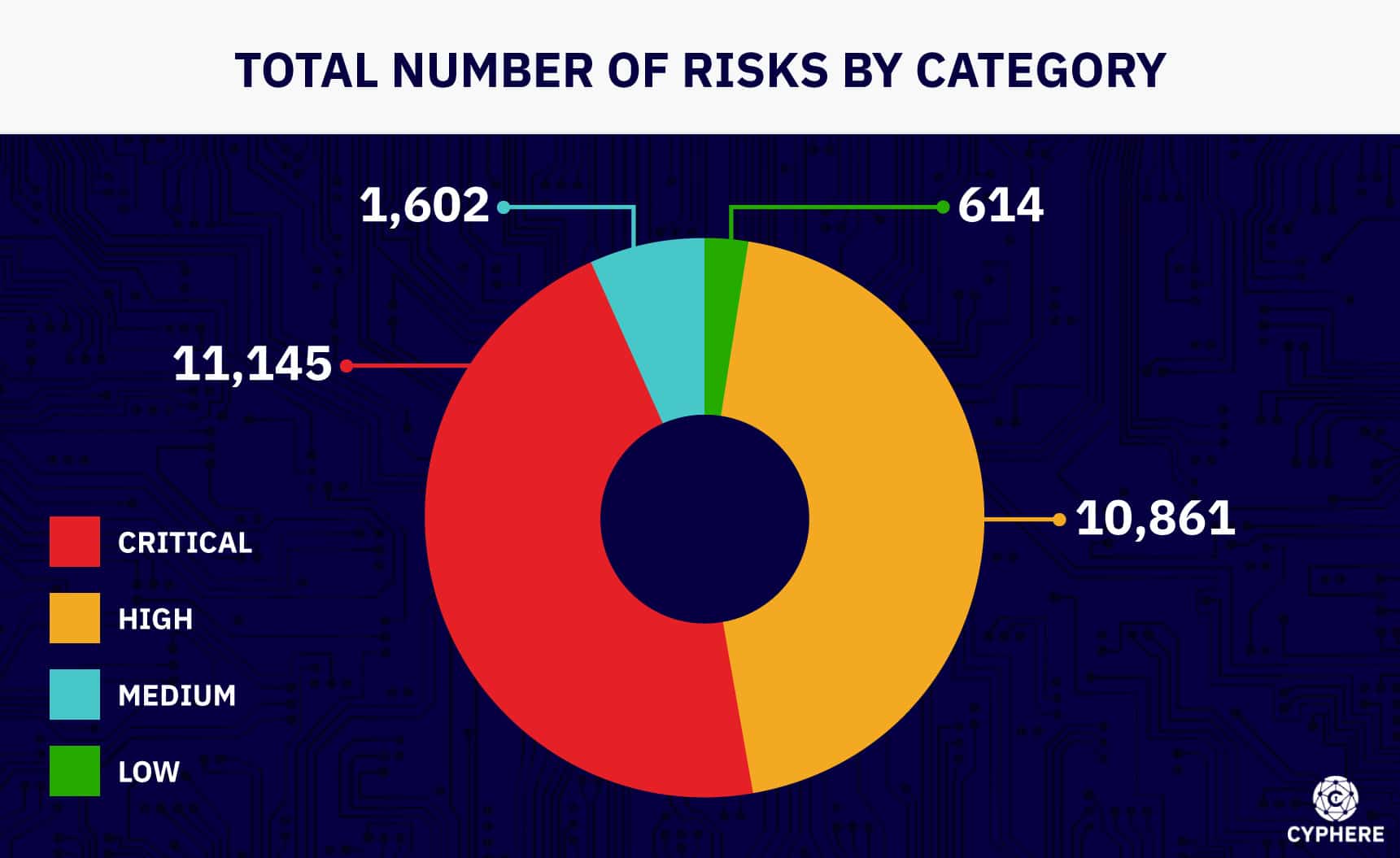
Social engineering statistics – Infographic

Overview – Social engineering statistics
In 2022, many researchers and businesses conducted surveys to uncover the most common attack types, and some of them revealed the following data.
- LookingGlass Cyber and ISACA state that social engineering attacks are the top cyber threat today.
- According to a study, about 98% of cyber-attacks involve social engineering and phishing in some way.
- Another survey of security researchers reports that more than 12 million spear phishing and social engineering attacks took place, impacting more than 17000 organisations.
- Security researchers also report that over 700 organizations fall victim to social engineering attacks yearly.
- On average, social engineering attacks cost companies approximately 130,000 USD through money theft or destruction of data.
- A survey by some security researchers mentions that only 27% of organizations practice social engineering awareness training.
- In its Cost of Data Breach 2022 report, IBM states that the global annual cost of a breach resulting from social engineering attacks has increased from 4.1 million USD.
- In the same report, IBM also states that it took almost 270 days (approximately nine months) for organizations to:
- Identify the breach – 201 days on average.
- Contain to the violation – 69 days on average.
- In its Data Breach Investigation Report 2022, Verizon states 82% of data breaches and cyber-attacks involve a human error or the human element as the leading cause.
- In their State of Cybersecurity Trends Report 2022, Arctic Wolf Networks report that 90% of the attacks and cyber threats target an organisation’s employees instead of its IT systems.
- Verizon reveals that out of 2,249 reported social engineering attacks, 1,063 resulted in the data being disclosed.
- In the same report, Verizon mentions that in the data breaches due to social engineering, 24% of the data was Personally Identifiable Information (PII).
- In the same report, Verizon disclosed that 63% of the data was authentication credentials.
- According to a survey by Cyber Security Hub, about 75% of cyber attacks and cyber threats to organizations were social engineering or phishing.
- KnowBe4 observed that up to 90% of data breaches involve social engineering.
- According to ZDNet, IT professionals fall victim to social engineering attacks 40 times yearly.
- Verizon’s survey showed that 69% of Public Administration breaches involve one or more types of social engineering attacks.
- In 2020 61% of organizations fell victim to social engineering scams and attacks. In 2021, this number increased to 74%.
- In contrast to the abovementioned figures, only 27% of the organizations practice social engineering awareness training and campaigns.
Social Engineering Types
Social engineering comes in various forms. The most common types of social engineering attacks and techniques are listed below:
Phishing
A form of social engineering attack that involves a fake email from a legitimate source asking for confidential and sensitive data and information, stealing authentication credentials, financial gain, or delivering malware.
Just like social engineering, phishing also comes in various forms. Spear phishing attacks are among the most common attack types of the same.
The only difference between phishing and spear phishing attacks is that the former may target any individual or business, while the latter only targets specific individuals, organizations or businesses.
Social engineering statistics involving phishing
Phishing ranks as one of the most occurring and most dangerous attack vectors in the world of cyber security.
- The Anti-Phishing Work Group recorded over 10 million phishing attacks in just the first quarter of 2022 alone, with a steady increase in the following quarters.
- According to a survey by Proofpoint, only 53% of the employees succeeded in correctly defining phishing scams and phishing attacks.
- According to CISCO, at least one person in approximately 86% of organizations clicked on a phishing link in 2021.
- According to a report by Tessian, 96% of all phishing attacks use malicious email attachments as the primary attack vector.
- Swiss Cyber Institute delineates that LinkedIn messages account for 47% of social media phishing attacks.
- CISCO, in another report, states that 90% of data breaches are linked to phishing attacks.
- According to a study by Forbes, phishing email ranks as the top attack on small businesses.
- KnowBe4, in their annual 2022 Phishing report, states that 43% of bank employees did not succeed in passing a phishing test.
- Google reports over 2 million phishing websites in the year 2021.
- 84% of phishing sites have SSL Certificates, which make them look trustworthy and legitimate.
- According to another research, there are almost 75x more phishing sites than malware sites.
Vishing statistics
A social engineering and phishing attack involves calling individuals over the phone to harvest sensitive and confidential data and information.
Although vishing seems a bit old-fashioned, it remains one of the top threats to cyber security in the social engineering attacks category.
Here are some facts and figures about vishing:
- In India, 93.5% of spam calls were related to either sales or telemarketing.
- When individuals were asked whether they knew about vishing, only 24% of them could define it correctly.
- A study reveals that
- 59.4% of the individuals who fell victim to vishing attacks were men,
- 38.3% were women, and
- 2.3% preferred not to disclose their gender.
- Brazil has been the most targeted country for vishing.
- Yorkshire and Humber remained the most targeted vishing points for the people living in the United Kingdom.
- Over 59.4 million in the United States fell victim to vishing attempts in 2021.
- 23% of the vishing victims lost their money.
- On average, 31 spam calls were received by individuals living in the United States in 2021.
- According to a report by PhishLabs, vishing attacks increased to a horrific 554% in 2021.
- A spammer in India made over 202 million spam calls in 2021.
SMishing
Like phishing, SMishing is a form of social engineering involving text messages or SMS (Short Message Service) to steal data and information and deliver and install malicious software.
Some SMishing statistics
Given the growing reliance on smartphones, the number of smishing attacks is expected to continue to grow, making individuals and organizations an attractive target for cybercriminals who use smishing as a tool to steal sensitive information.
Hence, individuals and organisations must stay informed about the dangers of smishing and implement robust security measures to protect themselves from these attacks.
- Approximately 378,509,197 smishing messages were received and sent in April 2022.
- Around 2,649,564,381 smishing attempts per week were made in April 2022.
- According to RoboKiller, a spam text messaging prevention service, more than 11.6 billion spam texts were sent to mobile phone users in the United States in March 2022.
- RoboKiller also reports that 26% of spam texts pretended to be delivery notifications.
- According to a study by Tessian, 36% of people fell victim to a smishing attempt and have fulfilled the attacker’s demands or clicked on suspicious links.
- Safety Detectives, in a report, states that the most common smishing attack involves some tax refund.
- The Federal Trade Commission, in 2021, received 378,119 complaints about spam text messages, including smishing attempts.
- Proofpoint reports that only 23% of North America’s total population could correctly define and explain smishing.
- A survey shows less than 35% of people worldwide know about smishing.
- The Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) reports that losses worth 54 million USD were due to phishing, vishing and smishing attempts on around 240,000 victims in 2020.
Dumpster diving
This involves physically searching through a person’s trash to find information that can be used in a social engineering attempt.
Impersonation
This involves posing as someone else, such as a trusted authority figure, to access sensitive information or systems. It is also referred to as identity theft.
Watering-hole attack
This involves compromising a website or service frequently visited by the target individuals, allowing the attacker to gather information or spread malware.
Shoulder surfing
This involves observing someone’s personal information, such as passwords or credit card numbers while entering them into a device or system.
Social engineering statistics – Some real examples of social engineering attacks in the recent times
MailChimp data breach – January 2023
In January 2023, MailChimp became aware of unauthorized people accessing their support tools.
How did it happen?
A specially crafted social engineering attack was carried out on MailChimp employees and contractors, which resulted in the attacker harvesting their authentication credentials.
Impact
After getting the authentication credentials, the attacker accessed the internal administration and customer support tool, which resulted in cyber attackers accessing the data of approximately 133 customers.
The Uber Hack – September 2022
Uber suffered an attack in which the threat actor compromised Uber’s internal network and accessed confidential reports. The attacker presented evidence of a successful breach by posting multiple screenshots.
How did it happen?
The cybercriminal informed that they social engineered an employee and got access to Uber’s VPN credentials. After getting VPN access, they could scan Uber’s internal network and operate as an authorized user.
Impact
The attack compromised the internal network and provided access to Uber’s bug bounty reports.
Twilio: Employee and customer account compromise – August 2022
In August 2022, Twilio fell victim to a classic social engineering and smishing attack and noticed unauthorized access to information related to some Twilio customer accounts. The attacker was able to gain access to some of Twilio’s internal systems and access customer data.
How did it happen?
Twilio employees received smishing messages informing the users that their password had expired, and they needed to update it or that there had been a change in their schedule. The smishing messages contained malicious URLs like “twilio-sso” and “twilio-okta”.
The URL redirected the users to a login page that impersonated Twilio’s sign-in page.
Impact
According to the incident report by Twilio:
- The incident impacted the accounts of 209 out of over 270,000 customers and 93 out of almost 75 million Authy end users.
- Twilio reports that the threat actors did not access the API keys, authentication tokens, or Twilio customers’ console account credentials—no evidence related to this.
Phishing attack on the US Department of Labor (DoL)
In January 2022, the US DoL fell victim to a credential-harvesting spear phishing attack that allowed the attacker to social engineer the users into giving up their credentials.
How did it happen?
The attacker spoofed the actual DoL’s email domain (dol.gov), used a domain that looked like one related to DoL (dol-gov.com), and sent out phishing emails containing a PDF document asking the recipients to bid on a government project.
The PDF document had a “Bid Now” button which had a malicious link embedded in it. Upon clicking the link, the users were redirected to phishing sites that seemed legitimate DoL sites.
Impact
The employees of the Department of Labor were social engineered to give up their Office 365 credentials.
Dropbox data breach due to phishing
In October 2022, Dropbox suffered from a successful phishing attack, resulting in the attacker gaining access to some code repositories.
How did it happen?
The attacked impersonated CircleCI, a code integration and development platform, sent phishing emails to social engineer Dropbox’s employees and harvested authentication credentials and codes.
Impact
The attacker gained access to Dropbox code repositories and API keys used by the employees of Dropbox.
Marriott International breach – July 2022
Marriott International suffered a social engineering attack, allowing the attacker to access 20GB of files, documents and information.
How did it happen?
The attacker used social engineering to trick an associate employee at a single Mariott hotel into giving the attackers access to the associate’s computer.
Impact
The incident allowed threat actors to access 20GB worth of information, including some non-sensitive internal business files and credit card information. Approximately 300-400 users were affected by this breach.
Morgan Stanley client accounts breached as a result of social engineering – March 2022
Morgan Stanley Wealth Management, a wealth and asset management division of Morgan Stanley, in early 2022 reported that a few of its customers’ accounts were compromised in a social engineering attack.
How did it happen?
The incident resulted from a vishing attack, where the attacker impersonated to be from Morgan Stanley and convinced the targeted victims to give out sensitive information such as financial details and authentication credentials.
Impact
Morgan Stanley stated in the incident report that the attacker successfully breached their client’s accounts and electronically transferred money to their bank accounts using the Zelle payment service.
Parting thoughts
Most organizations invest colossal capital to secure their IT infrastructure, but high-edge security technologies only act as a product if businesses do not invest in security awareness training. Social engineering attacks cost is increasing massively. Tools can not identify the social engineering tactics and targeted attacks, but a well-aware individual can.
References
- https://www.zdnet.com/article/average-organization-targeted-by-over-700-social-engineering-attacks-each-year-report/
- https://firewalltimes.com/social-engineering-statistics/
- https://docs.apwg.org/reports/apwg_trends_report_q1_2022.pdf
- https://www.proofpoint.com/us/resources/threat-reports/state-of-phish
- https://www.humanize.security/blog/news/144-cybersecurity-statistics-for-2022#Eighth
- https://webtribunal.net/blog/social-engineering-statistics/#gref
- https://earthweb.com/vishing-statistics/
- https://www.phishlabs.com/blog/vishing-volume-increases-554-in-2021/
- https://www.consumerreports.org/money/scams-fraud/smishing-a-silly-word-for-a-serious-fraud-risk-a8541743941/
- https://www.safetydetectives.com/blog/what-is-smishing-sms-phishing-facts/
- https://earthweb.com/smishing-statistics/
- https://terranovasecurity.com/cyber-security-statistics/#smishing_statistics
- https://www.itbrew.com/stories/2022/05/02/text-based-smishing-attacks-are-ramping-up
- https://www.thesslstore.com/blog/social-engineering-statistics/
- https://www.twilio.com/
- https://www.tessian.com/
- https://www.cshub.com/
- https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/
- https://get.eftsure.com.au/
- https://www.comparitech.com/
Harman Singh is a security professional with over 15 years of consulting experience in both public and private sectors.
As the Managing Consultant at Cyphere, he provides cyber security services to retailers, fintech companies, SaaS providers, housing and social care, construction and more. Harman specialises in technical risk assessments, penetration testing and security strategy.
He regularly speaks at industry events, has been a trainer at prestigious conferences such as Black Hat and shares his expertise on topics such as ‘less is more’ when it comes to cybersecurity. He is a strong advocate for ensuring cyber security as an enabler for business growth.
In addition to his consultancy work, Harman is an active blogger and author who has written articles for Infosecurity Magazine, VentureBeat and other websites.