
As artificial intelligence (AI) becomes more and more prevalent in society, it is also making its way into the world of cyber security. AI can be used in a number of ways to help improve cyber security, including by automatically detecting and responding to threats, improving network efficiency, and helping to identify vulnerabilities. In this blog post, we will discuss some of the ways that AI is changing cyber security and how it can help your business stay safe online.
Artificial intelligence is changing the landscape of cybersecurity. The advantages in this article show that by implementing AI systems, organisations will be able to increase their speed of detection, and response and be more proactive in predicting and handling emerging threats.
What is Artificial intelligence(AI)?
Artificial intelligence is a type of intelligence displayed by machines, as opposed to the natural intelligence displayed by humans and other animals. AI applications can analyse data and make decisions on their own, without human intervention.
AI is achieved through evaluating the processes and researching the patterns of the human brain. These threat investigations result in the creation of intelligent software, systems or AI powered solutions.
AI learns over time, handling a lot of data
Foundations of AI are based on what is known as the Turing test in AI. The Turing test in AI is a method of determining whether or not a machine can exhibit behaviour that is indistinguishable from a human. If the answer to this question is yes, then the machine is said to have passed the Turing test and is considered intelligent.
The three main components of AI are:
- Learning in AI is the process of acquiring new knowledge or skills from experience.
- Reasoning is the ability to draw logical conclusions from a set of premises.
- Self-correction is the ability to identify and correct errors.
What is the role of Artificial intelligence in cyber security?
The role of AI for cyber security is to help organisations reduce the risk of breaches and improve their overall security posture. AI works in cyber security by learning from past data to identify patterns and trends. This information is then used to make predictions about future attacks. AI powered systems can also be configured to automatically respond to threats and fight cyber threats in quicker timescales.
As the corporate attack surface continues to develop and evolve, analysing and enhancing cyber threats and cyber attacks is no longer a human-scale challenge. Depending on the size of your organisation, up to several hundred billion time-varying signals must be processed to calculate risk appropriately.
In response to this unprecedented challenge, AI tools and methods such as neural networks have evolved to assist information security teams in protecting sensitive information, reducing breach risk and improving their security posture with more effective and efficient threat detection and threat removal features.
Use of machine learning in cyberspace
Machine learning is a subset of AI that uses algorithms to automatically learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed.
It is mainly used in cyber security for two purposes:
- Anomaly detection: Machine learning can be used to automatically detect anomalies, such as unusual user behaviour or unexpected network activity, that could indicate a security threat. For example, products such as crowdstrike, darktrace and many others are using this.
- Classification: Machine learning can be used to automatically classify data, such as emails or files, into categories (such as spam or malware) so that they can be dealt with more efficiently.
AI / Cybersecurity conundrum – Potential downsides
We are all good and loud about the use of AI to solve security issues.
What if adversaries AI is up for win?
Cybercriminals can train AI systems or false data inputs into data-sets used by AI. This will enable them to create more realistic and sophisticated attacks. In addition, AI can be used to automate attacks, making it possible for a single actor to carry out large-scale attacks.
AI systems are also susceptible to being fooled by so-called “adversarial examples” – inputs that have been specifically designed to trick the system into making an incorrect classification. For example, an image of a stop sign that has been slightly altered so that it is no longer recognisable as a stop sign could fool an autonomous car into thinking it is something else, such as a yield sign. This could potentially lead to disastrous consequences.
As AI becomes more widely used in cybersecurity, it is important to consider the potential risks and how they can be mitigated. One way to do this is by ensuring that AI systems are “explainable” – that is, they can provide a justification for their decisions. This will help to ensure that decision-making is transparent and accountable and will help to prevent adversarial examples from being used to trick the system.
In conclusion, AI based cybersecurity systems are showing great promise in helping organisations. However, it is important to be aware of the potential risks and take steps to mitigate them.
How is AI used in security?
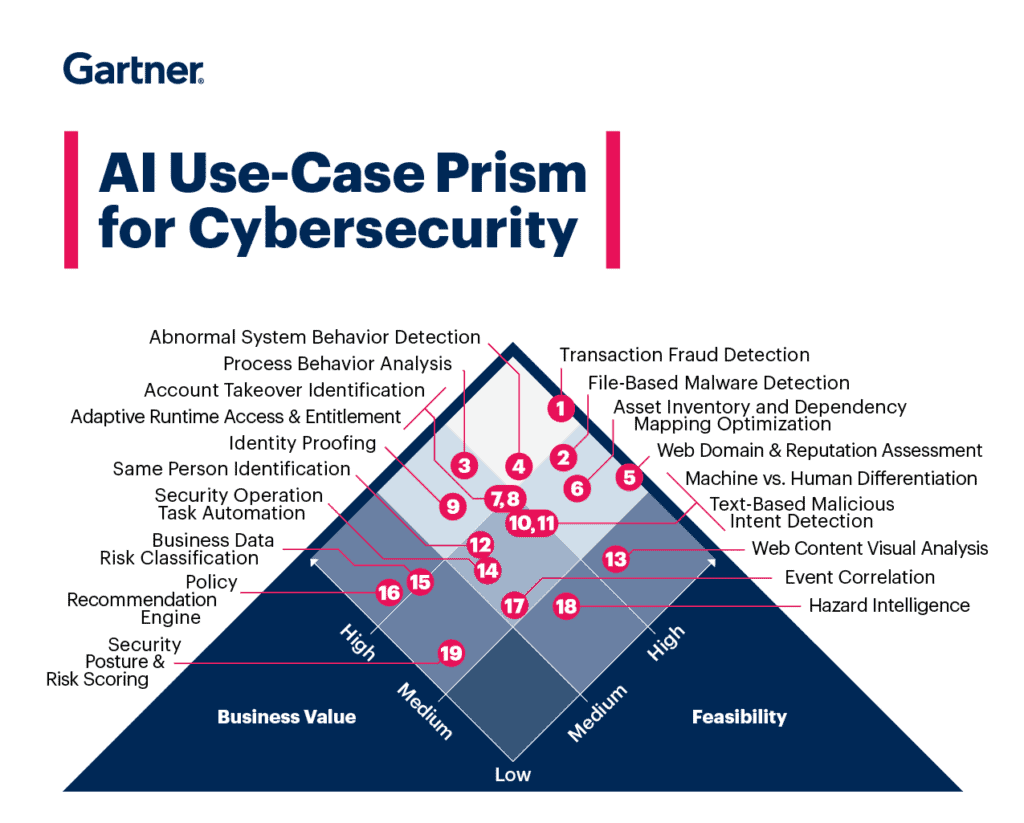
There are several good use cases for AI in cybersecurity. Starting with the researchers or think-tanks, here’s a good example of Gartner’s use-case prism for cybersecurity. Hyperautomation is a much-discussed topic since Gartner’s prediction – this means that another magnitude of automation will kick in on top of generic next-gen AI systems. This involves incorporating AI/ML along with automation + quality assurance to ease the managing of alerting and incident response work. In essence, it will help businesses augment no-code or low-code security at scale and improve business agility and DevOps strategies.
Here is the list of applicable examples for security services and cloud security:
- Transaction fraud detection
- File-based malware detection
- Process behaviour analysis
- Abnormal system behaviour detection
- Web, domain & reputation assessments
- Asset inventory & dependency mapping optimization
- Account takeover identification
- Adaptive runtime access & entitlement
- Identify proofing
- Machine vs human differentiation
- Text-based malicious intent detection
- Same person identification
- Web content visual analysis
- Security operation task automation
- Business data risk classification
- Policy recommendation engine
- Event correlation
- Hazard intelligence
- Security posture & risk scoring
Here are examples of how AI in cyber security will reduce the time in identification, detection and reaction to cybersecurity threats:
Automated malware detection and prevention
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning can assist to stay up with cybercriminals, automating threat detection, and responding more effectively than traditional software-driven or manual methods. Machine learning techniques can be used to improve malware detection by combining numerous types of data from anti-malware components on the host, network, and cloud.
A previously unknown sample could be a new file in malware and ransomware attack detection helping endpoint protection mechanisms. Its hidden property may or may not be malicious. Similarly, malware that can avoid detection is not guaranteed to be caught every time.
This does not mean that all malware attacks will be stoppable using AI. The model is a mathematically structured collection of rules that underpin data attributes.
Phishing and Spam Detection
Deep learning uses enormous amounts of data to train a deep neural network, which subsequently learns how to classify images or complete other tasks on its own over time.
Even for attack operations that are relatively loosely characterised, deep learning models can obtain excellent accuracy rates. They’re used to detect not-safe-for-work and other images as well as spam email and phishing attack efforts.
Deep learning was employed by Google to detect difficult-to-detect image-based emails, emails with hidden content, and communications from newly formed domains. This could help with the detection of phishing attacks sophistication including Internet traffic patterns linked to spamming.
Faster and accurate anomaly detection – SIEM and SOAR platforms
AI can identify both malicious and benign anomalies within network traffic data in near-real-time. By applying machine learning algorithms to network traffic data, it is possible to detect previously unknown attacks as well as known attacks that have been modified to evade detection.
SIEM and SOAR systems increase the security infrastructure of organisations. Advanced analytical approaches and machine learning are used to identify the alarms, which require fine-tuning due to occurrences of false positives.

SOAR is the engine that handles the remediation and reaction to SIEM warnings. It is intended to assist security teams in automating the response process by collecting alerts, managing cases, and responding to SIEM’s never-ending notifications.
Threat intelligence capabilities are one of its solutions, giving security teams more visibility into other threats not just across computer systems, but also IOT devices and other integrations.
Searching for Zero-Day Exploits
In a zero-day attack, criminals infect computers with malware by exploiting a software flaw that has yet to be patched by a manufacturer. However, current discussions and developments in AI may be of assistance.
Deep learning architectures can be used to find hidden or latent patterns and become more context-aware over time, which can help identify zero-day vulnerabilities or activities. Natural language processing can scan source code for dangerous files and flag them. “Generative adversarial networks,” which can learn to mimic any data distribution, could also be useful in identifying complex flaws.
Increases the speed of detection and response
The first step in defending your company’s network is to detect threats. It would be ideal if you could rapidly detect things like untrustworthy data. It will protect your network from permanent damage.
Integrating AI with cyber security is the greatest way to detect and respond to threats in real-time. Artificial intelligence examines your entire system for risks. Unlike human intelligence alone, AI in cyber will detect risks early, leading to faster and more accurate security alerts and making cybersecurity professionals’ jobs efficient.
Detection of new threats
Predictive analytics to identify anomalous behaviour or patterns of activity is one of the top use cases of AI in cybersecurity. Cybercriminals are always looking for new ways to exploit systems. AI can help identify these new threats before they cause any damage.
Reduce the number of false positives
When you have too many false positives, it takes away from the time you could be used to actually fix real issues. But with AI in charge of identifying security incidents, you can reduce the number of false positives and get your team back to work quickly.
AI can quickly analyse a large number of events and identify a wide range of security risks, from malware to threat identification of risky behaviour that could lead to phishing or malicious code download with the help of data science. These systems improve with time, leveraging on previous attacks to identify new sorts of attacks in the present. Behaviour histories help AI recognise and respond to departures from established norms by creating profiles on users, assets, and networks.
AI systems are being trained to detect malware, execute pattern recognition, and detect even the tiniest characteristics of malware or ransomware attacks before they enter the system using advanced algorithms.
With natural language processing, AI can provide higher predictive intelligence by scraping articles, news, and studies on cyber dangers and curating material on its own. AI-based security solutions can provide the most up-to-date knowledge of global and industry-specific threats, allowing you to make more informed prioritising decisions based on what is most likely to be used to attack your systems rather than what could be used to attack your systems.
Detecting Bots
Bots now account for a significant portion of internet traffic, and they can be deadly. Bots can be a serious threat, from account takeovers using stolen passwords to fraudulent account creation and data fraud. Manual reactions are ineffective against automated threats. AI and machine learning aid in the analysis of website traffic and the differentiation of good bots, bad bots, and humans.
By analysing behavioural patterns, firms can learn what a typical user journey looks like and what a risky uncommon journey looks like. We can decipher the purpose of their web traffic from here, allowing us to keep ahead of the evil bots.
Prediction of Breach Risk
AI systems assist in determining the IT asset inventory, which is a complete and accurate list of all devices, users, and apps with varying levels of access to various systems. Now, taking into account your asset inventory and threat exposure (as stated above), AI-based systems can forecast how and where you’re most likely to be hacked, allowing you to plan and devote resources to the most vulnerable locations.
This breach risk prediction would help organisations stay prepared to limit the impact and break attack chains. Further, using the risk data you may set and modify policies and procedures to reinforce your cyber resilience using prescriptive insights from AI-based analysis.
Conclusion
It’s clear that AI can be a powerful tool in the fight against cybercrime. By automating many of the tasks currently carried out by human security analysts, we can reduce the number of false positives and speed up the process of detection and response.
It’s important to be aware of the potential risks associated with using AI, and take steps to mitigate them. What do you think? Is AI for cyber security a benefit or an affliction?
Harman Singh is a security professional with over 15 years of consulting experience in both public and private sectors.
As the Managing Consultant at Cyphere, he provides cyber security services to retailers, fintech companies, SaaS providers, housing and social care, construction and more. Harman specialises in technical risk assessments, penetration testing and security strategy.
He regularly speaks at industry events, has been a trainer at prestigious conferences such as Black Hat and shares his expertise on topics such as ‘less is more’ when it comes to cybersecurity. He is a strong advocate for ensuring cyber security as an enabler for business growth.
In addition to his consultancy work, Harman is an active blogger and author who has written articles for Infosecurity Magazine, VentureBeat and other websites.












